Diabetes is a prevalent chronic disease impacting millions globally, cutting across ages and demographics with its profound health implications. Understanding its complexities—from causes to treatment options—forms the foundation for effective management and prevention.
Whether navigating the distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes or seeking insights into lifestyle choices and alternative therapies like homeopathy and Ayurveda, this comprehensive guide equips you with the essential knowledge to empower proactive health decisions and foster a healthier future.
Understanding the Growing Problem
Diabetes is a chronic illness that’s becoming more common around the world. As of now, over 463 million people are living with diabetes, and this number is expected to reach 578 million by 2030. In the U.S., more than 34 million people have diabetes, with many more undiagnosed. This rise in diabetes cases is concerning for health professionals, policymakers, and individuals alike.
So, what exactly is diabetes? It’s a condition where the body either can’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Without proper insulin function, blood sugar levels remain high, which can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness. Diabetes also impacts mental and emotional well-being, significantly affecting quality of life. Understanding and managing diabetes is crucial to prevent these severe complications.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of diabetes. We’ll discuss its types, causes, symptoms, and treatments. We’ll also look at how lifestyle choices affect diabetes and share strategies for prevention. By the end, you’ll have valuable insights into maintaining a healthy lifestyle and minimizing the risk of developing diabetes.
What is Diabetes and Why is it Increasing?
Diabetes is a condition where the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin is impaired, leading to high blood sugar levels. The number of people with diabetes has risen sharply over the past few decades, with the World Health Organization reporting an increase from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014, mostly due to type 2 diabetes. The modern lifestyle—marked by poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress—plays a significant role in this rise. Genetic factors and environmental influences also contribute.
Different Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This type is caused by an autoimmune response and requires regular insulin treatment. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type, often linked to lifestyle factors. Symptoms are similar to type 1 but can develop more gradually. This type can sometimes be managed with lifestyle changes and medication.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and can pose risks to both mother and baby if not managed properly.
- LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults): A slower-progressing form of type 1 diabetes.
- MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young): A rare form of diabetes that runs in families.
Impact of Lifestyle on Diabetes
Diet, exercise, and stress management are crucial in managing diabetes. Eating a balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels, while regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity. Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can also have a positive impact.
Prevention and Precautions
Early detection through regular health check-ups is key. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits—such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress—can prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps keep diabetes under control and prevents complications.
Treatment Options
- Allopathy: Conventional medical treatment, including medication and insulin therapy.
- Homeopathy: Alternative remedies focusing on natural treatments.
- Ayurveda: Traditional Indian medicine using herbs and lifestyle changes.
- Naturopathy: Natural therapies to support overall health.
- Physical Exercise: Essential for managing diabetes and improving overall health.
Common Questions and Concerns
- Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding the differences and which is more severe.
- Type 2 Diabetes with Peripheral Neuropathy: What it means and how to manage it.
- Is Watermelon Good for Diabetes? Exploring the benefits and concerns.
- Childhood Diabetes: Recognizing early signs and symptoms.
- Insulin Pen: A convenient tool for insulin administration.
Living Healthy and Preventing Diabetes
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing diabetes. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and consistent exercise are essential. By understanding diabetes and taking proactive steps, individuals can lead healthier, happier lives.
In our previous discussion on diabetes 10 early symptoms, we explored how early detection plays a crucial role. Read more
Factors That Can Cause Diabetes
Diabetes is a complex condition influenced by various factors. Understanding these can help in preventing or managing the disease. Here’s a look at some key factors:
Family History and Genetics
Having a family member with diabetes increases your risk of developing the condition. Genetic mutations affecting insulin production or function can also contribute to diabetes.
Lifestyle Choices: Diet, Exercise, and Weight
Unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, and being overweight are significant risk factors. A diet high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, along with a sedentary lifestyle, can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Environmental Influences: Pollution, Stress, and Sleep Problems
Environmental factors like air pollution can increase the risk of diabetes by causing inflammation and oxidative stress. Chronic stress and sleep problems, such as sleep apnea, can also disrupt blood sugar regulation.
Age, Ethnicity, and Income Level
The risk of diabetes increases with age, particularly after 45. Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and American Indians, are more prone to diabetes. Lower income levels can limit access to healthy food, exercise, and healthcare, raising the risk of developing diabetes.
By understanding these factors, you can take steps to reduce your risk or manage diabetes. This includes making healthy lifestyle choices, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress effectively.
Different Types of Diabetes: Understanding the Variations
Diabetes is a complex disease affecting millions worldwide, with several distinct types. Understanding these different types helps in better managing, preventing, and treating the condition.
Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Type 1 diabetes, or insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to high blood sugar levels due to a lack of insulin. Causes are still unclear but involve genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and weight loss. Diagnosis is made through blood tests like the HbA1c test.
Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, involves insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin, leading to high blood sugar. It’s often linked to obesity, lack of exercise, and a poor diet. Symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, slow healing of wounds, and dark skin patches. Diagnosis involves blood tests like the fasting plasma glucose test and the HbA1c test.
Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes during Pregnancy, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
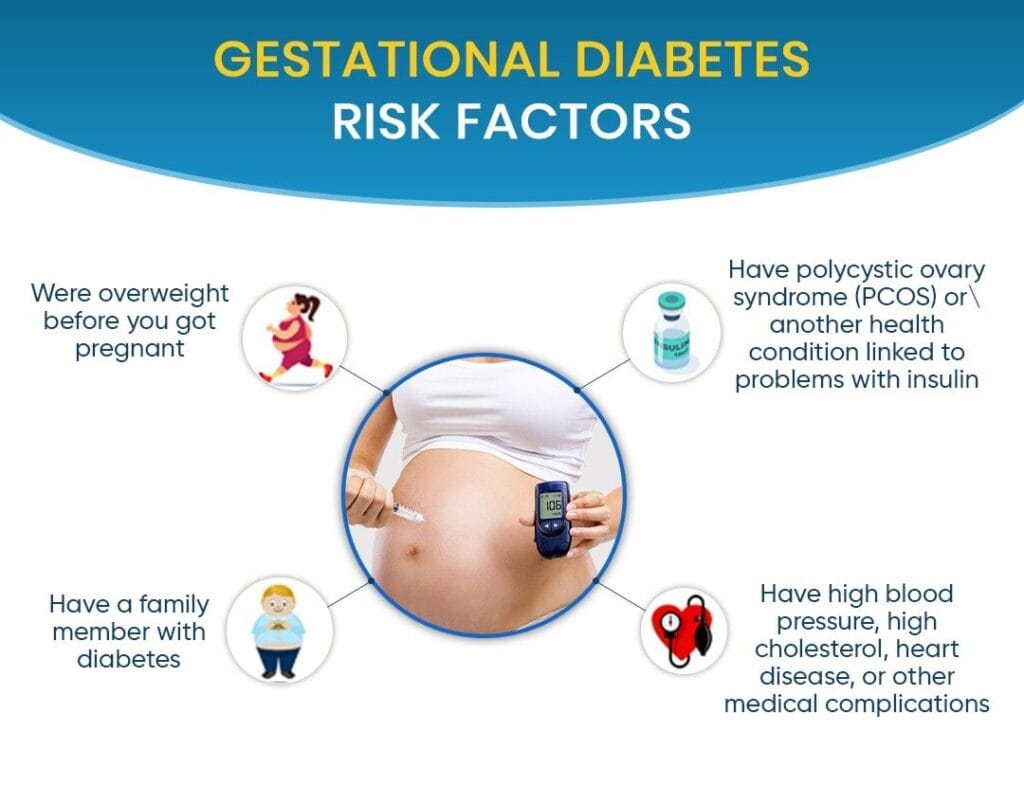
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester, due to hormonal changes causing insulin resistance. Symptoms are similar to those of type 2 diabetes but can also include nausea and vomiting. Diagnosis is typically done with a glucose screening test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
LADA Diabetes: Symptoms and Diagnosis
LADA (latent autoimmune diabetes in adults) is a type of type 1 diabetes that develops in adults, often after age 30. It involves a gradual decline in insulin production and requires blood tests and autoantibody tests for diagnosis. Symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
MODY Diabetes: Symptoms and Diagnosis
MODY (maturity-onset diabetes of the young) is a rare form caused by genetic mutations affecting insulin production. It often appears in young adults and requires genetic testing for diagnosis. Symptoms are similar to type 2 diabetes, including increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Understanding the different types of diabetes is key to effective management and prevention. By recognizing their unique characteristics, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the disease and improve their overall health.
How Lifestyle Affects Diabetes
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in managing and preventing diabetes. From diet to exercise and stress management, these daily decisions significantly impact blood sugar levels and overall health.
Balanced Diet
A healthy diet is key to managing diabetes. Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps keep blood sugar levels stable. For example, watermelon, rich in fiber and antioxidants, can be beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes. On the flip side, a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can worsen the condition and lead to weight gain, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Regular Exercise
Exercise is essential for diabetes management. Activities like walking, running, or swimming can lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. For those with type 2 diabetes, regular physical activity can also alleviate symptoms and prevent complications such as peripheral neuropathy.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress. Ensuring you get enough sleep and engaging in relaxing activities also support better stress management and overall health.
Other Lifestyle Changes
Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, and getting regular check-ups are important steps in managing diabetes. These changes can improve overall health and help in controlling blood sugar levels.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can effectively manage diabetes, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance your quality of life. At Chatterlane.com, we believe that informed choices lead to better health outcomes. Understanding how lifestyle affects diabetes empowers you to take control of your health.
Prevention and Precautions: Key Steps to Managing Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively requires a proactive approach, focusing on lifestyle habits and regular health check-ups. Here are some practical steps to prevent and manage diabetes:
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are crucial for early detection of diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and body mass index (BMI), you can identify potential risks early and take action to manage or prevent diabetes. Annual check-ups are recommended, especially if you’re over 45 or have a family history of diabetes.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
A healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing and managing diabetes. Focus on these three key areas:
- Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Adequate sleep and engaging in activities you enjoy can also help reduce stress.
Monitoring and Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
If you have diabetes, regularly monitoring and controlling your blood sugar levels is vital. Use a glucometer to track your levels and adjust your diet and exercise routine as needed. Work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, which may include medication or insulin therapy.
By adopting these preventive measures and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can reduce the risk of developing diabetes or manage its symptoms effectively. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and a healthy lifestyle is your best defence against diabetes.
Treatment Options for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Approach
Managing diabetes effectively requires understanding and utilizing various treatment options to find what works best for you. Here are some of the main approaches:
Allopathy: Traditional Medical Treatments
Allopathic treatments, or conventional medicine, focus on managing blood sugar levels through medications and lifestyle changes. Common medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin injections. These treatments help control blood sugar but may have side effects.
Homeopathy: Alternative Remedies
Homeopathy takes a holistic approach, treating the individual rather than just the symptoms. Remedies like uranium nitricum and syzygium jambolanum aim to balance the body’s natural rhythms. This approach can be a good alternative for those seeking natural methods, though it may not be suitable for everyone.
Ayurveda: Traditional Indian Treatments
Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of medicine, emphasizes balance in the body’s energy forces (doshas). Treatments often include dietary changes and herbal remedies such as turmeric and cinnamon to promote digestion and regulate blood sugar.
Naturopathy: Natural Treatments
Naturopathy focuses on natural remedies and lifestyle changes. Treatments might include dietary modifications, herbal supplements, and techniques like acupuncture. This approach aims to address the underlying causes of diabetes and improve overall health.
The Importance of Physical Exercise
Regular exercise is crucial for managing diabetes. Activities like walking, cycling, and yoga can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week.
By exploring these treatment options—whether allopathic, homeopathic, Ayurvedic, or naturopathic—and incorporating regular exercise, you can manage diabetes more effectively and reduce the risk of complications. A comprehensive approach tailored to your needs can help you live a healthier life.
Common Questions and Concerns About Diabetes
Diabetes comes with many questions and concerns. Here are some of the most common ones to help you understand and manage the condition better:
Which is Worse, Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?
People often wonder which type of diabetes is worse. Both types have their challenges. Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy as it is an autoimmune disease. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors and can sometimes be managed with diet and exercise. Both types can lead to serious complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage if not managed properly.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes with Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a common complication of Type 2 diabetes, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent or slow its progression. The diagnosis code for Type 2 diabetes with peripheral neuropathy is E11.40.
Is Watermelon Good for People with Type 2 Diabetes?
Watermelon is a healthy fruit that’s low in calories and rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. People with Type 2 diabetes can enjoy watermelon in moderation as part of a balanced diet, but it’s essential to be mindful of portion sizes due to its natural sugar content.
Early Signs of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
Type 2 diabetes is increasingly seen in children. Early signs include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If you notice these symptoms in your child, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Using an Insulin Pen for Easy Insulin Management
For those who require insulin therapy, insulin pens are a convenient and easy way to manage insulin doses. They are portable, user-friendly, and help reduce the risk of dosing errors, making them a great option for both new and experienced users of insulin therapy.
By understanding these common questions and concerns, you can better control your diabetes management and lead a healthier, happier life.
Living Healthy and Preventing Diabetes
Living a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing diabetes, and making a few simple changes can significantly lower your risk of developing this chronic disease. With over 422 million people worldwide affected by diabetes, it’s important to take steps to protect your health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential. Focus on eating whole foods, fruits, and vegetables, and limit sugar and saturated fats. Physical activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can improve insulin sensitivity and help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help you monitor your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Early detection of potential health risks allows you to take action before they develop into full-blown diabetes.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is crucial for overall health. Some studies suggest that water, including watermelon juice, can help regulate blood sugar levels. However, always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Support Systems
If you have diabetes, having a support system can make a big difference. Online resources like Chatterlane.com, support groups, and healthcare professionals can provide valuable help and encouragement.
Treatment Plans
For those diagnosed with diabetes, working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan is important. This may include medication, like insulin therapy, or alternative therapies such as homeopathy, Ayurveda, or naturopathy.
By making healthy lifestyle choices, staying informed, and seeking support, you can manage diabetes and live a healthy, fulfilling life. Remember, taking control of your health today can help you avoid diabetes and its complications, leading to a happier, healthier future.
Conclusion: Empowering a Healthy and Active Life
Understanding and managing diabetes is essential for a healthy, active life. With diabetes affecting millions globally, it’s important to take proactive steps for prevention and management.
Types and Causes of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 is an autoimmune disease requiring insulin therapy. Type 2, often linked to lifestyle factors, can be managed and sometimes reversed through diet, exercise, and weight management.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, and vegetables while limiting sugar and unhealthy fats is crucial. Regular physical activity, like walking, cycling, or swimming, helps regulate blood sugar and improve overall health. Stress management and staying hydrated also play significant roles in diabetes prevention.
Regular Health Check-ups
Routine check-ups help monitor blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, allowing early detection and management of potential health risks.
Support Systems and Treatment
For those living with diabetes, having a support system is invaluable. Friends, family, healthcare professionals, and online resources like Chatterlane.com can provide the necessary support and encouragement. Managing diabetes may include medications like insulin therapy or exploring alternative treatments like homeopathy, Ayurveda, or naturopathy.
For more information on Diabetes, It’s types, causes and medication please read
Future Prevention
Preventing diabetes involves making informed lifestyle choices. By prioritizing a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetes. Promoting health and wellness empowers individuals to take control of their health and live fulfilling lives.
In conclusion, understanding diabetes and taking proactive steps can lead to a healthier, happier life. By making informed choices and seeking support, you can manage or prevent diabetes effectively. Let’s commit to a healthier future today.


Comments
3 responses to “Diabetes: It’s Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments”
[…] more Health Related Blogs, Read: Diabetes, Negative Thoughts, Teenage […]
[…] Might Enjoy:Depression Symptoms, Causes and Treatments:Victory Over Cancer: Are We Close to Winning?Diabetes: It’s Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Effective TreatmentsPractical ways to deal with negative thoughtsTeenage Depression Unveiled: A Powerful Guide for […]
[…] types, causes, and medical treatment options in more detail, you can also refer to this helpful Diabetes: It’s Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments that covers it […]